How To Create Your Own Run Commands In Windows (4 Methods)
Run command is used to directly open an application or document whose path is known. However, you can create some pre-defined commands to open applications. So today we will discuss how to create your own Run Command in Windows. Go through the full post to know about it
HowTo Create Your Own Run Commands In Windows
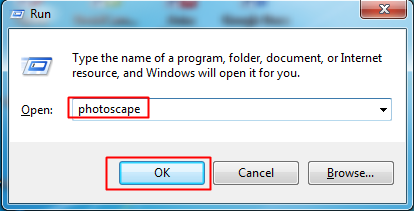
Commonly run commands are executed through the run box, which opens by pressing Windows button + R. However, you can only access some of the programs, not all. So in the below steps we will tell you a method by which you can easily create a run command of any software according to your wish. Just follow the below steps to proceed.
Steps To Create Run Commands In Windows
The Simple Way:
This is the easiest way which you can use to create Run command on your Windows computer. Here you don’t need to alter any Windows settings. You just need to CUT/PASTE the shortcut files to windows folder to create RUN command.
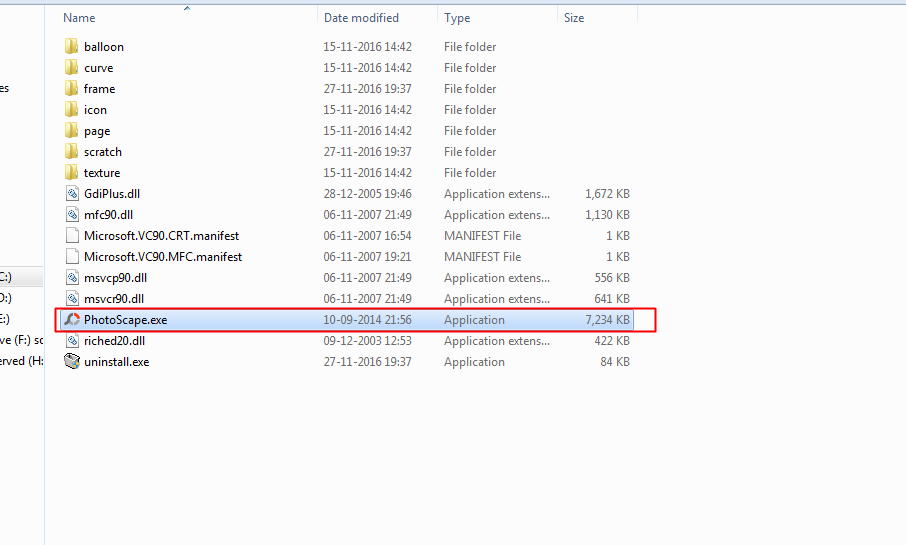
Step 1. First of all, you need to select the app you want to create a shortcut.
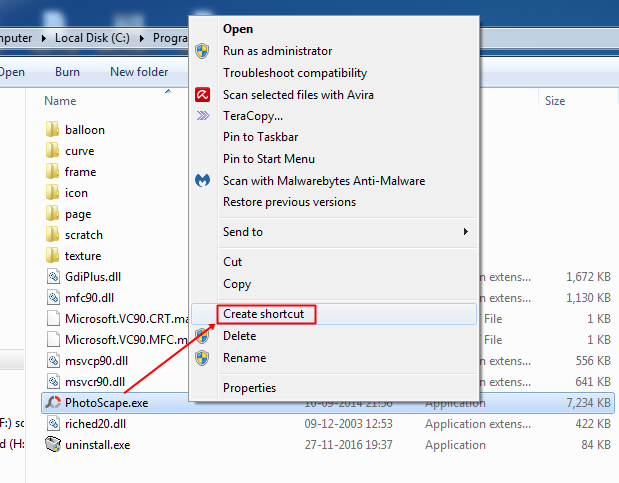
Step 2. Now right click on the app and then click on “Create shortcut”
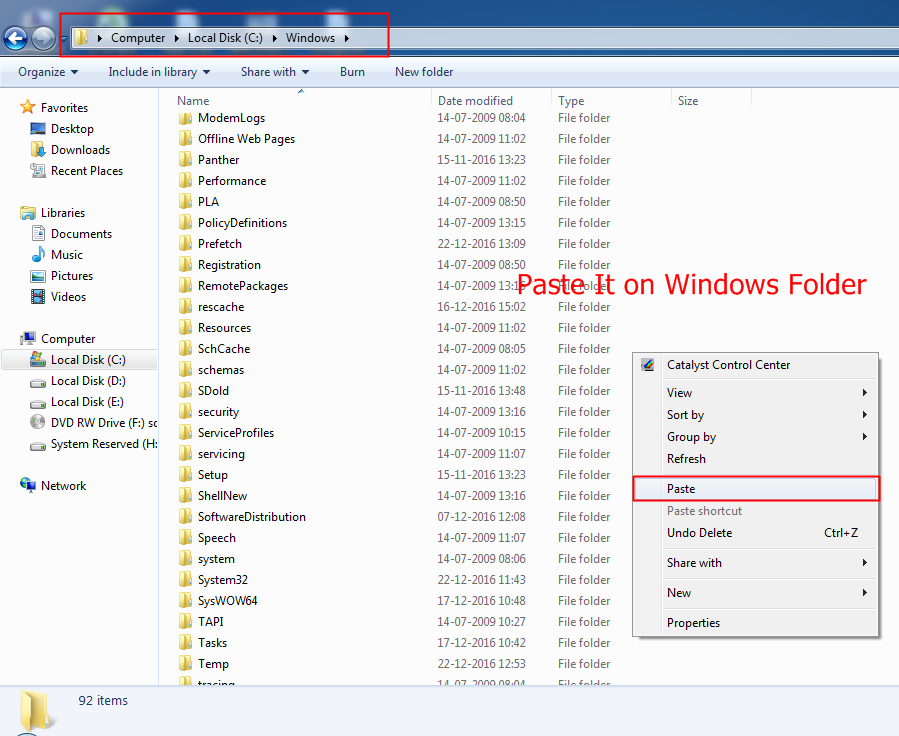
Step 3. Now you need to move the file to Windows folder (My Computer> Local Disk:C> Windows)
Step 4. That’s it! You have created the shortcut file for that particular app. Simply press “CTRL+R” and in the run box type the name of the shortcut file that you moved into the Windows folder, it will open.
Manually Creating The Shortcut File:
Step 1. Firstly, select the software whose run command you want to create. Here we will be selecting Mozilla Firefox. You can select any of the software that you use frequently while working on a computer.
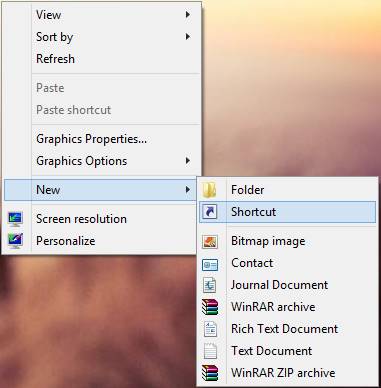
Step 2. Now right click on the desktop and select new and then shortcut.
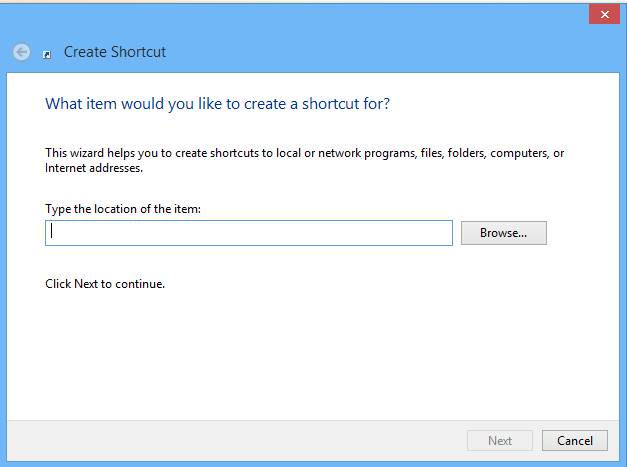
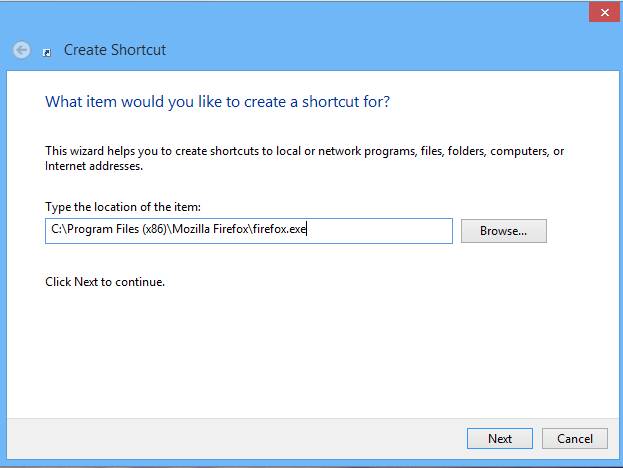
Step 3. Now a dialog box will appear and then it will ask you for the path you want to select to access any of your installed application.
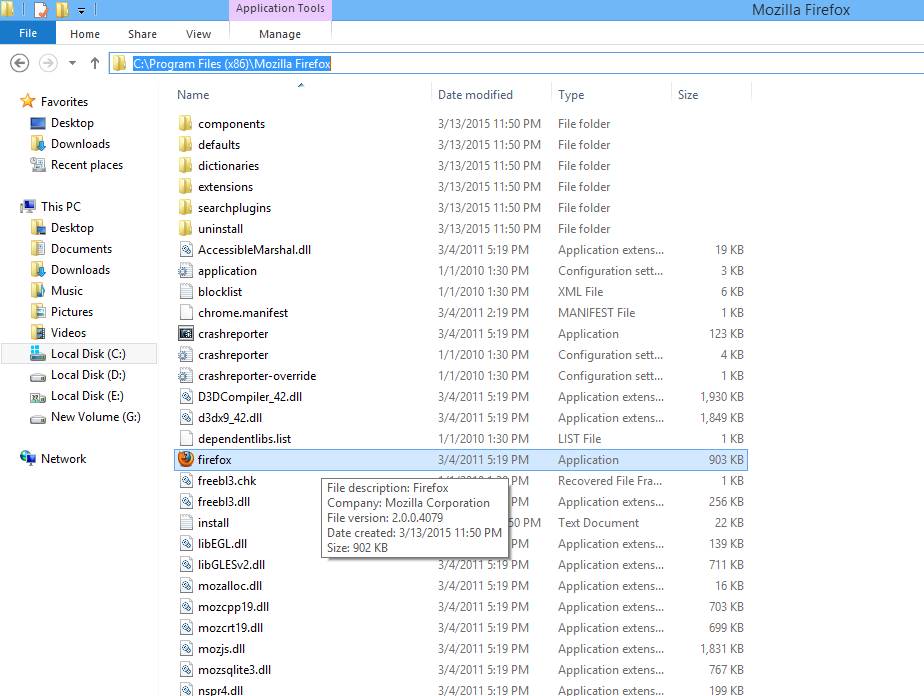
Step 4. Now you have to give the path of the application, and we know that our all programs are installed in Program Files folder of C drive, after opening C drive click on the folder of your application that you want to open, here we will open a folder of Mozilla Firefox.
Step 5. Now locate the address of the application like C:Program Files (x86)Mozilla Firefoxfirefox.exe. Now paste this path in your shortcut dialog box and proceed by clicking next. Now give it any desired name and your folder is created.
Now paste this path in your shortcut dialog box and proceed by clicking next. Now give it any desired name and your folder is created.
Using AddToRun
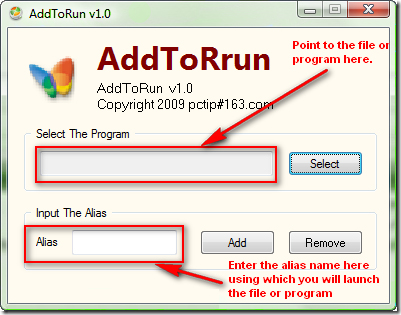
AddToRun is a small utility that will allow you to open any file or application from the Start Menu’s Run Command dialog box (WIN+R). It has a very simple interface which will allow you to select a file and assign it an alias or friendly name.
You simply need to press Windows Key + R at the same time that will bring AddTorun utility. You need to browse the program and set the name in “Alias” and you can run it from Run Prompt
Method 4: Using Registry Edit
You can also create your own RUN command by adding keys in Windows Registry. However, if you are going for this method, then I suggest you take a backup of the registry.
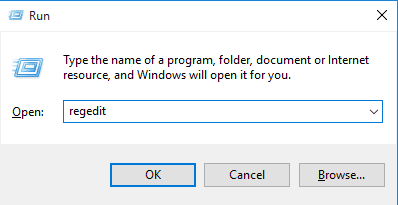
Step 1. First of all, open the Run command (Windows Key + R) and then type regedit and hit enter.
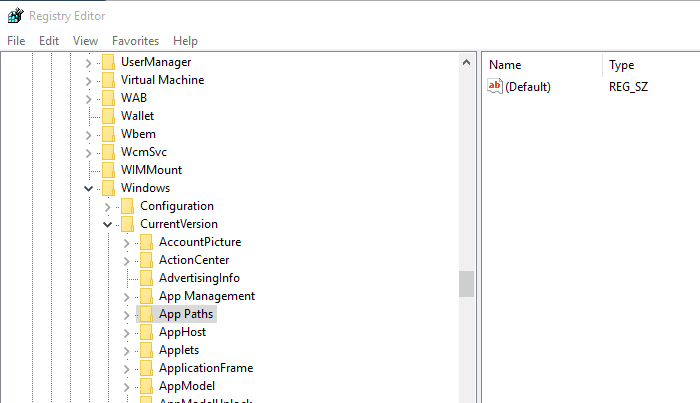
Step 2. Now you need to navigate to the following section:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE > SOFTWARE > Microsoft > Windows > CurrentVersion > App Paths
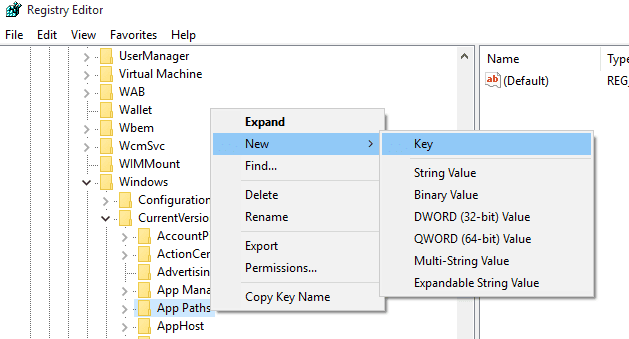
Step 3. Now you need to right click on the “App Paths” and then choose New > Key
Step 4. Type the name of the key and .exe. For example, i am about to create the shortcut for Google chrome, so I need to create a command like Google chrome.exe
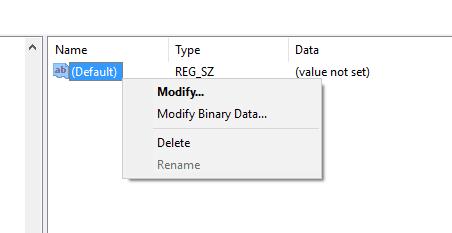
Step 5. Now in the right panel, you need to right click on “Default Key” and then select the option “Modify”
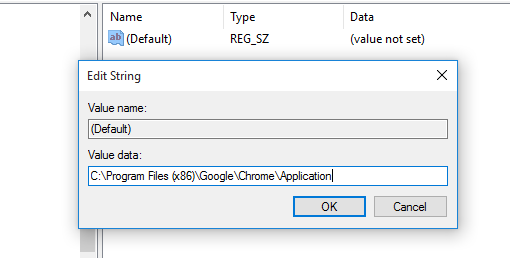
Step 6. Now in the value data field, enter the URL of the Google chrome executable file.
That’s it, you are done! from now on whenever you will type Chrome in run command it will open Google chrome browser for you.

.png)





